The DOM: The Missing Piece in My Web Development Journey
When I got into Web development I thought that HTML and CSS worked wonders. It was really cool to me as I could make buttons, pretty layouts, play around with different colours and fonts yada yada. Things got real when I discovered that it goes beyond just the pretty page, which actually did nothing much and was just there as a static page, I discovered about JavaScript and something called DOM. It’s interesting to discover that what you thought was cool actually is not all that’s there but there are things on a deeper level to it. But then I was like, is it really like that that my buttons are not working to their highest potential but just redirecting to another static page ? I thought that’s how a button actually works, but after learning about JavaScript and DOM I found that’s the base level performance and there’s so much more to it !
Let me give you a dive into my journey of finding JS and DOM.
What’s DOM ?
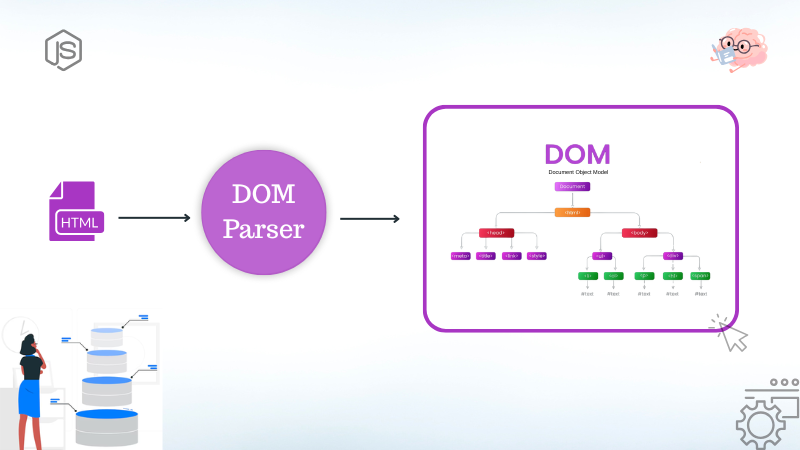
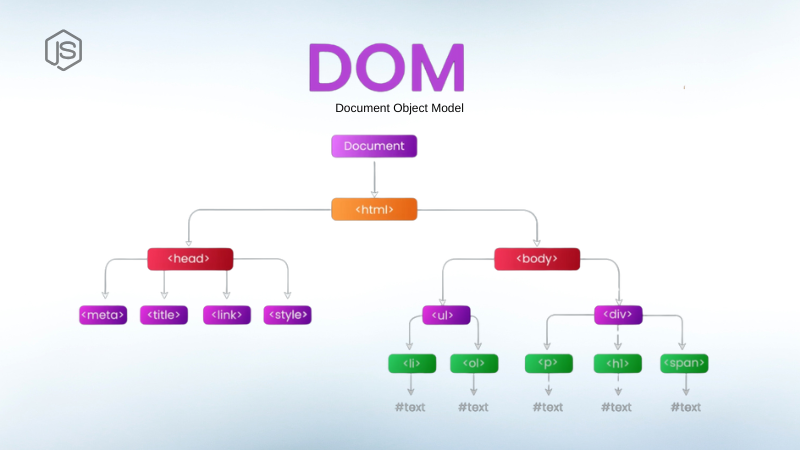
You insert so many things into your web page like headings, divs, images, animations, etc, how do you think the browser understands and organizes them ? This is where DOM comes into play. DOM actually stands for Document Object Model and is a blueprint of the web page that the browser creates behind the scenes. The browser takes the raw HTML and turns it into a structured tree where each element like headings, paragraphs, buttons, etc are the nodes. The fun part is you can use JavaScript to access and modify it in real time i.e. through JavaScript you can talk to the DOM and tell it what to do. This makes the web page interactive instead of static pages.
Moral of the story is that you create a web page using HTML, style it with CSS then the browser takes the raw HTML, reads, analyses and then structures it as a tree with elements of the HTML file as the nodes and it’s done in such a way that it makes sense for rendering and interaction. This process is known as Parsing and this structured representation of the entire document is known as a Document Object Model (DOM). Now that the framework is done you can traverse through the tree and also manipulate it in real time using JavaScript.
How Can You See the DOM of Any Website?
You don’t need to imagine the DOM — you can actually see it for real !
- Right-click anywhere on a webpage → click Inspect
- Or just hit
Ctrl + Shift + I(orCmd + Option + Ion Mac) - Then click on the Elements tab
And there ! You’ve unlocked the live DOM.
What you’re seeing there might look like regular HTML, but it’s actually the browser’s version of your page — the DOM. You can:
- Hover over elements to see them highlighted on the page
- Change text, colors, styles (just for fun !)
- Even delete or add stuff right there
What Does the DOM Look Like ?
When people say the DOM is a “tree”, don’t worry — you’re not missing some fancy graphic in DevTools. The DOM doesn’t look like a literal tree with nodes and branches.
What you see is nested HTML, like this:
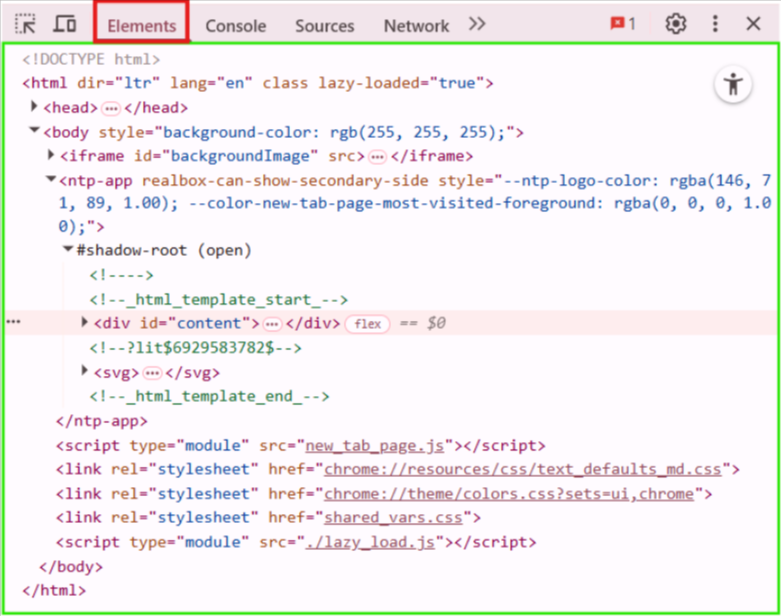
It’s the browser showing you the real-time DOM that it built from the original HTML. Though it might look like the HTML code it’s not.
- The DOM is not the raw HTML.
- It’s not a literal tree with roots, nodes and branches either though.
- It’s just a structured, interactive version of the web page that the browser understands and renders.
Your browser builds a tree structure of elements. It’s like:
<html>as the root (of the tree)<head>and<body>are its children- Elements inside
<body>(like<h1>and<button>) are their children… and so on.
It’s just like a family tree or a data structure tree — each element is a node, connected to other nodes via branches. The tree itself is invisible, but the nesting gives it away.
It’s the browser’s version of your web page.
DOM & Data Structure
You probably have seen trees and learnt about their structure in your Data Structure class — you know, the one with roots, children, siblings and all the branching stuff?
Well… DOM is like its cool, browser-based cousin — that doesn’t live in textbooks but actually appears in actual websites!
Each element of your page (HTML) becomes the node in this tree:
<html>→ Root node- Tags inside it → Children nodes
- Elements on the same level inside the same element → Siblings
- Elements on the same level but not inside the same element → Cousins
- Tags at the very end with no children → Leaf nodes
Though the literal tree is not what you get to see as the DOM, it’s still the browser’s version of the tree and thus how you walk through it matters.
Why Bother Learning the DOM?
Great question—one I asked myself too.
Actually the creation and designing of your site has nothing to do with the DOM at all. But if you want your website to do more than just sitting there as static pages you need it, specifically you need interaction with the DOM.
Here’s why learning the DOM matters:
- For buttons that actually do something other than just redirecting you to another static page.
- You can update your site on the fly without reloading!
- Most modern frameworks(React, etc) are built around the DOM.
- You can react to the users in real time like respond to scrolls, show or hide things, etc.
HTML & CSS Without JavaScript
HTML and CSS together do a fine job in designing a beautiful web page, with buttons, links, pretty layouts, etc but what it can’t compensate for is the dynamic feature. The web page created using HTML and CSS can be as beautiful as possible with everything in it but it will be static and not very interactive for the users. It’s like a beautiful poster that once printed can’t be modified. To make the web page dynamic and interactive we need the third component that’d be JavaScript.
How JavaScript Interacts With The DOM?
When the browser is done creating a structured representation for a HTML or XML code i.e. the Document Object Model, we need a medium to interact with it and for that we have JavaScript. JS acts as an interface to interact with the DOM and also the magic stick that allows you to make modifications to the DOM in real time. Through JavaScript you can traverse through the entire tree (the structured representation) and manipulate it too.
Does DOM Exist Without JavaScript?
While learning all these I was really curious about what happens to DOM if there exists no JavaScript? The answer to it actually makes sense. Actually the browser reads the HTML file, analyses and structures it regardless of the existence of the JavaScript. JS is just the way to interact with the DOM, their existence is not dependent on each other though. The browser creates a DOM for all HTML and XML files even if there’s no JavaScript to interact with it, it just sits there.
How JS Interacts With the DOM?
The HTML builds the structure, CSS styles it and makes it visually appealing. When a webpage loads, the browser reads the raw HTML, analyses it and creates the DOM i.e. a tree-like structure for visual representation of the HTML.
JavaScript doesn’t go knocking on the raw HTML — it talks to this DOM structure. Like:
document.querySelector("h1").textContent = "Hello!";
What this does is - it finds <h1> element in the DOM and changes its text. It doesn’t affect the HTML file itself but just changes the way the browser sees it that too in real time.
Common DOM Actions
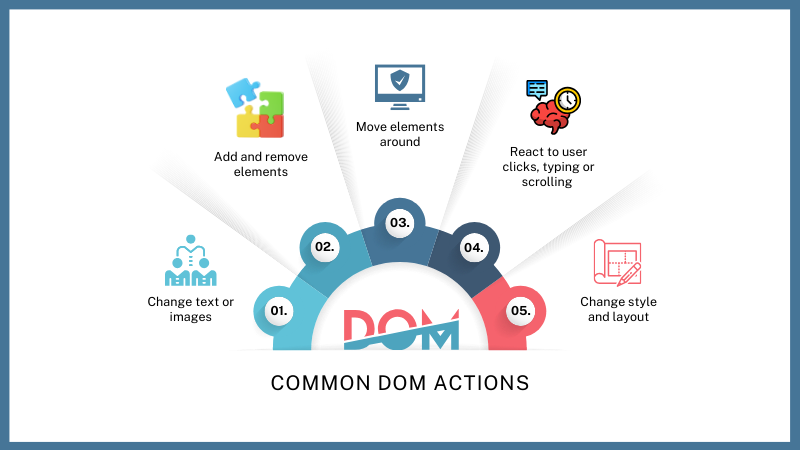
Some common actions that you can perform by using JavaScript to interact with the DOM are:
- Change text or images
- Add and remove elements
- Move elements around
- Change style
- React to user clicks, typing or scrolling
And you can do all these in real time, without affecting the HTML file.
Final Verdict
DOM may sound a bit tricky at the beginning but it’s really simple. It’s just the browser’s version of your HTML file. You make study notes in a way you understand, right? This is the browser’s notes to understand the structure of the webpage (in the form of a tree… that is not literally what you see as DOM though). And this structure is understood, accessed and manipulated using JavaScript. The DOM exists even if there’s no JavaScript because it is just the interface to interact with the DOM and has no effect on the existence of the DOM.
The DOM makes your webpage more organised and interactive, instead of a static page you get a dynamic one. Using JavaScript you can take real time actions on the DOM, without harming the HTML file. Learning the DOM is honestly a must if you’re stepping into the world of real web development.
And the best part? You don’t need to memorize everything — just start small, mess with things, and let it build naturally.
No magic. No hype. Just how the web works — and now, you know it too.